Become a Backyard Beekeeper – Help Save the World!
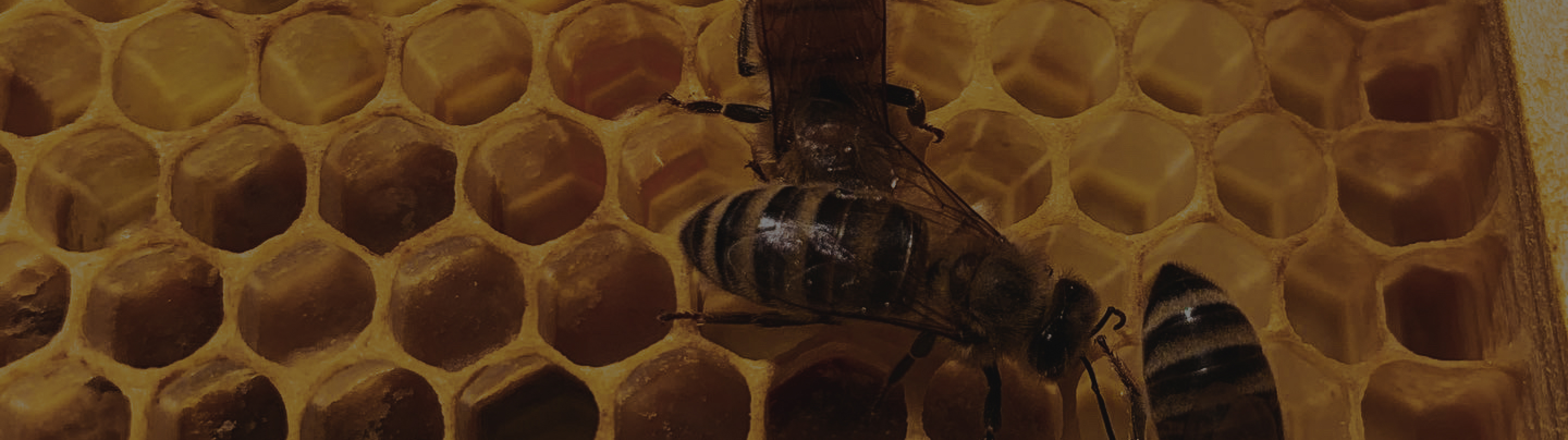
Did you know that honeybees play a significant role in pollinating plants and flowers, which helps the environment? Honeybees not only help produce honey and other bee products, but they are also instrumental in spreading pollen to fertilize plants. By ensuring the survival of honeybees, we can help keep our planet healthy and thriving. Learn more about how these fantastic creatures help our ecosystem below.
Six ways honeybees help the environment
Honeybees are essential for several reasons. There are six ways to show the importance of honeybees to the environment.
-
Pollination
Honeybees play a critical role in pollinating crops and other plants. In collecting nectar and pollen, they transfer pollen from the male reproductive organ or stamen of one flower to the female reproductive organ or pistil of another. These actions fertilize the plant to produce fruits, vegetables, and nuts. About one-third of the human food supply depends on insect pollination, most of which is accomplished by bees.
-
Source of food and honey
Honey is a sweet food made by bees from the nectar they collect from flowers. It’s a natural sweetener in many foods and beverages and has several health benefits. Approximately one-third of the food we eat relies on pollination from bees, making them essential to our survival. Without honeybees, we would lose a significant food source, and our planet would not be as diverse or vibrant.
-
Biodiversity – beekeeping pollination
Bees are one of the most important groups of pollinators, and they are essential for the health of many ecosystems. By pollinating plants, bees help to ensure that these plants can produce fruits, vegetables, and nuts. This helps to support the animals that depend on these plants for food.
Honeybees are also crucial for the pollination of crops. In the United States, bees pollinate about $15 billion worth of crops each year. This includes fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
-
Biodiversity – beekeeping agriculture
Without bees, many of these crops would not be able to grow. This would have a significant impact on the food supply for both humans and animals.
Various factors, including habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change threaten the bees. This makes it more critical than ever to protect bees and their habitats.
-
Propolis
Propolis is a sticky substance collected by bees from trees and plants. It’s used in the hive to seal cracks and repair damage. It also has antibiotic and antifungal properties.
-
Royal jelly
Worker bees produce Royal jelly – a milky white secretion produced exculsively by worker bees. It’s fed to the queen bee and young larvae. Beeekeepers use Royal jelly as cosmetics and as a dietary supplement.
-
Use in treatment
There are several ways that bee venom can treat various medical conditions. Bee venom therapy, or apitherapy, is an alternative medicine that uses bee stings to treat various ailments.
This venom contains several medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and analgesic compounds. Bee venom also contains melittin, a compound shown to have antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal properties.
Final words
Honeybees are one of the most important insects in the world and Beekeepers play a vital role in agriculture by pollinating crops, and they also help to keep the environment healthy. Bees live in colonies of up to sixty thousand individuals, and each colony can travel up to four miles per day looking for food. Honeybees can survive in a variety of climates, and they can breed year-round. Honey is a valuable food source, and colonies produce wax that can be used to make candles and other items. Honeybees are an essential part of our ecosystem, and we should do what we can to protect them. Therefore, next time you see a bee buzzing around, remember that it’s doing its part to help our planet! Honeybee School courses and beekeeper kits can help you help our environment.